Estonian Subsea Cable Landscape: Outages, Resiliency & Sabotage Suspicions - Part 1

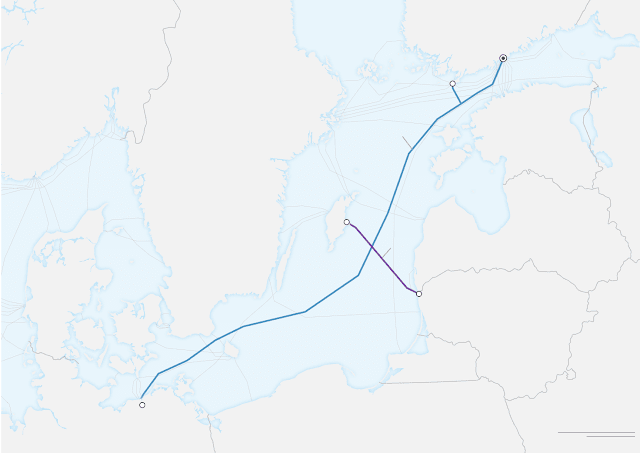
Estonia is a small Baltic nation with 1.4 million inhabitants. It has eight subsea fibre optic cables plus several power interconnectors. It is a large number given its land mass and population. Over the last several years Baltic Sea outages have been frequent with many in the Nordics pointing their finger at Russia. Many of these outages have involved cables landing in Estonia. However, the Baltic Sea is extremely shallow. Its average depth is 52 to 55 meters. So cables in these waters are extremely vulnerable to fishing vessels and cargo ships dragging anchors. If they are not buried deeply in protected sea lanes, damage is inevitable. The other factor is the Russia shadow fleet. Europe is weaning itself off Russian gas imports with the figure falling from 8 billion cubic meters per month in early 2022 to 2 billion cubic meters today. When the war began, sanctions forced European headquartered global shipping lines to either stop serving Russia or place restrictions on acc...